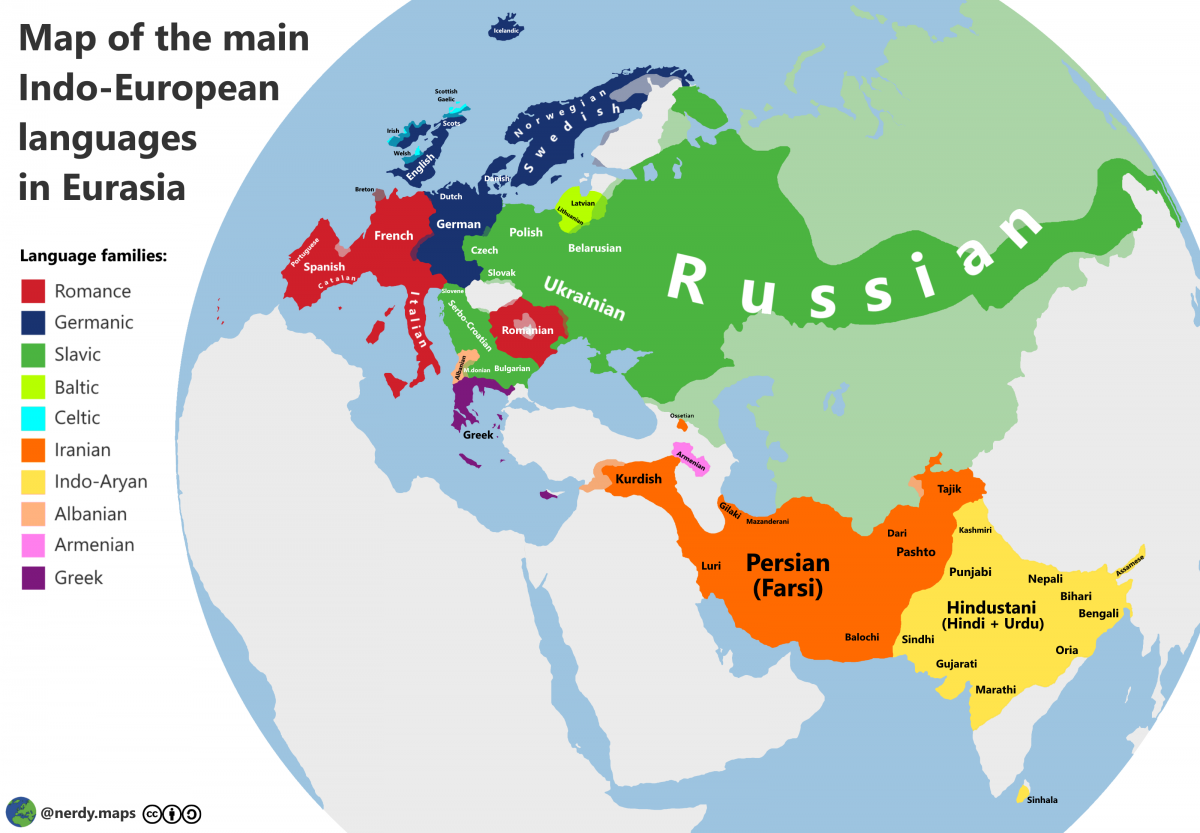
Indo-European languages, a diverse family encompassing over 400 languages spoken by more than 40% of the global population, have intrigued linguists and historians for centuries. Recent landmark studies have shed light on their origins, tracing them back approximately 6,500 years to the Caucasus Lower Volga region in present-day Russia. These studies, driven by ancient DNA research, identify the Yamnaya culture as key players in the dissemination of this ancestral tongue, revealing the complex genetic ancestry of languages across Europe and into Asia. As researchers delve deeper into the interplay between language, culture, and genetics, the exciting discoveries not only underscore the migratory patterns of the Yamnaya people but also illustrate the profound impact of these early populations on the development of modern civilizations. This groundbreaking work represents a significant leap in our understanding of how Indo-European languages came to shape the linguistic landscape we know today.
The exploration of the linguistic family known as Indo-European languages offers fascinating insights into human history and evolution. Often associated with ancient cultures such as the Yamnaya and regions like the Caucasus Lower Volga, the origins of these languages have been clarified through interdisciplinary research that combines linguistics, archaeology, and genetics. By studying genetic ancestry and employing ancient DNA methodologies, scholars have unraveled the migration paths of early peoples, enriching our knowledge of how languages spread across vast distances. The findings not only contribute to an understanding of the complex tapestry of human communication but also highlight the cultural exchanges that facilitated these developments. As this research continues to evolve, it poses new questions about the interconnectedness of ancient societies and their lasting legacies on contemporary languages.
Tracing the Origin of Indo-European Languages
The recent landmark studies published in Nature shed light on the origin of the Indo-European languages, a family that includes English, Spanish, and Hindi among its over 400 languages. Researchers have pinpointed the Caucasus Lower Volga region in present-day Russia as the birthplace of these languages, tracing them back to around 6,500 years ago. This discovery marks a significant turning point in our understanding of linguistic evolution, providing concrete DNA evidence from ancient populations that supports long-standing theories regarding the spread of these languages across Europe and beyond.
Understanding the origins of Indo-European languages entails delving into the rich tapestry of cultural and genetic history. Linguistic and archaeological research has suggested that speakers of the proto-Indo-European language flourished in the vast Eurasian steppe, particularly among the Yamnaya culture. Their nomadic lifestyle and innovations, including horseback riding and wagons, allowed them to traverse great distances, effectively spreading their language and culture into regions as far as India and the British Isles.
Caucasus Lower Volga: The Birthplace of Language Diversity
The Caucasus Lower Volga region serves as a critical geographic and cultural hub in the history of Indo-European languages. Genetic analyses indicate that the people from this area intermingled with various neighboring populations, contributing to the linguistic diversity we see today. The striking similarities among languages such as Greek, Latin, and Sanskrit have led researchers to conclude that these languages share a common ancestry tracing back to this ancient community.
Moreover, the studies draw attention to the genetic legacy left by the Caucasus Lower Volga people. This group’s interaction with other cultures, particularly during significant migration events, played a crucial role in shaping the demographic landscape of Europe and parts of Asia. Their migration patterns and social structures facilitated the dissemination of language, effectively laying the groundwork for modern language families.
The Yamnaya Culture and Its Linguistic Impact
The Yamnaya culture emerged as a significant player in the story of Indo-European languages. Researchers postulate that these nomadic pastoralists, known for their innovations in animal husbandry and transportation, took the proto-Indo-European language across vast territories. Their expansion from the steppes of modern Ukraine and Russia facilitated not only the spread of their language but also their agricultural practices and cultural traditions.
Archaeological evidence, including burial sites and artifacts, supports the idea that the Yamnaya culture was influential in the cultural and genetic shaping of populations in Europe. Their unique burial practices, such as the construction of kurgans, symbolize a rich cultural heritage that persists in modern European populations. By spreading across Europe, the Yamnaya facilitated cultural exchanges while solidifying their linguistic legacy in the heart of ancient societies.
Genetic Ancestry and Language Evolution
Recent advancements in ancient DNA research have unveiled profound insights into the genetic ancestry of contemporary European populations. Studies demonstrate that many modern Europeans can trace their roots back to a mix of ancestral groups, primarily influenced by the Yamnaya and other populations from the Caucasus region. These genetic markers reveal how language evolution is intricately linked with migration and demographic changes, emphasizing the shared heritage of Indo-European speakers.
The blending of cultures outlined by genetic studies supports the hypothesis that language is not merely a form of communication but a representation of shared identity and social cohesion. As ancestral groups such as the Yamnaya spread their language and customs, they simultaneously shaped the genetic landscape of Europe, resulting in significant shifts that can be tracked through generations.
Connecting Language with Archaeological Discoveries
The relationship between language and archaeology is exemplified in the study of Indo-European origins. Archaeologists have uncovered burial sites and artifacts that correspond to the timeline of language evolution, providing concrete evidence of cultural practices that shaped linguistic diversity. The examination of kurgans, for instance, offers a glimpse into the customs of the Yamnaya and their ancestors, linking these practices directly to the languages that emerged from this region.
These archaeological discoveries are pivotal in constructing a comprehensive understanding of the cultural context in which Indo-European languages developed. As researchers analyze artifacts, they uncover insights into daily life, social structures, and intergroup interactions, weaving a narrative that intertwines language evolution with cultural and historical developments.
The Role of Ancient DNA in Linguistic Studies
Ancient DNA research has revolutionized the field of linguistics by providing empirical evidence supporting historic linguistic theories. By isolating and analyzing genetic material from archaeological sites, researchers can trace the movements and interactions of ancient populations, revealing how these dynamics influenced the development of Indo-European languages. The blending of science and linguistics opens new avenues for understanding language origins and evolution.
Furthermore, the integration of genetic data enhances our ability to construct a nuanced narrative of human history. It elucidates how migrations and cultural exchanges have shaped linguistic landscapes, exposing the intricate web of relationships among various Indo-European languages. By examining genetic ancestry alongside linguistic development, scholars can paint a more comprehensive picture of our shared past.
Linguistic Similarities Across Indo-European Languages
The study of Indo-European languages reveals remarkable similarities that span across diverse cultures and regions. Linguists have noted consistent structural features, vocabulary, and phonetics that indicate a common ancestry. These similarities not only highlight the historical connections among languages such as Sanskrit, Greek, and ancient Latin but also emphasize the shared human experience across time and space.
Exploring these linguistic parallels helps to unravel the pathways of human migration and cultural exchange that have transpired throughout millennia. As researchers investigate the genetic and cultural factors that contributed to these similarities, a clearer picture emerges of how ancient peoples communicated and influenced one another, further enriching our understanding of human connections worldwide.
Challenges in Tracing Language Origins
While DNA evidence has provided remarkable insights into the origins of Indo-European languages, challenges remain in fully understanding the complexities of language evolution. Factors such as the preservation of ancient DNA, the fragmented nature of archaeological records, and sociopolitical barriers complicate the research process. For instance, the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war has had significant implications for collaborative research efforts, affecting access to archaeological sites and resources.
Additionally, linguistic evidence is often fragmentary, relying heavily on reconstruction methods that can only provide approximate insights into language relationships. While ancient DNA analysis offers a powerful tool for tracing ancestry, it must be complemented by linguistic and archaeological data to create a comprehensive understanding of language origins. This interdisciplinary approach is vital for piecing together the intricate puzzle of our linguistic heritage.
Future Directions in Indo-European Research
As researchers continue to uncover the origins of Indo-European languages, future studies will undoubtedly focus on integrating genetic, archaeological, and linguistic data in innovative ways. The continued analysis of ancient DNA will likely yield new insights into the migrations and cultural exchanges that shaped language evolution. Such research projects aim to deepen our understanding of the interconnectedness of human societies and the factors that influence language change.
Moreover, advancements in technology, including improved sequencing techniques and computational methods, are expected to enhance our capacity for analyzing ancient populations. As we gain better tools and methodologies, the future of Indo-European research looks promising, with the potential to uncover new connections and narratives that enrich our understanding of human history and cultural diversity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the origin of the Indo-European languages?
The origin of Indo-European languages can be traced back to the Caucasus Lower Volga people, who lived in what is now Russia around 6,500 years ago. This population is considered the earliest speakers of the proto-Indo-European language, which eventually diversified into over 400 languages today.
How did the Yamnaya culture contribute to the spread of Indo-European languages?
The Yamnaya culture, emerging from the Eurasian steppes, played a critical role in the dissemination of Indo-European languages. Approximately 5,000 years ago, the Yamnaya began spreading their language and culture from the lower Volga region all the way to areas like Mongolia and Ireland, contributing significantly to the genetic and linguistic landscape of much of Europe and parts of Asia.
What role does ancient DNA research play in understanding Indo-European languages?
Ancient DNA research has been pivotal in tracing the genetic ancestry of populations associated with Indo-European languages. Recent studies have utilized genetic data to identify links between the Caucasus Lower Volga people and subsequent Indo-European groups, aiding in reconstructing the historical migrations and language developments that shaped today’s linguistic families.
What is the relationship between the Caucasus Lower Volga people and the Yamnaya?
The Caucasus Lower Volga people are identified as the ancestors of the Yamnaya culture. Genetic evidence shows that these early inhabitants intermingled with other groups and laid the foundation for the future Yamnaya people, who are credited with spreading proto-Indo-European languages across vast regions of Europe and Asia.
How did the steppe hypothesis relate to Indo-European language origins?
The steppe hypothesis posits that the speakers of the proto-Indo-European language emerged from the Eurasian steppe. This theory gained traction in the 19th century and was supported by various archaeological and linguistic findings, aligning with the recent identification of the Caucasus Lower Volga people as a pivotal source of Indo-European languages.
What evidence supports the idea of a unified origin for Indo-European languages?
The recent studies that analyzed ancient DNA from various archaeological sites provide compelling evidence of a unified origin for Indo-European languages. They reveal genetic connections among the Caucasus Lower Volga people, the Yamnaya, and other ancient populations, showcasing the genetic continuum that links these groups and their languages.
What cultural practices did the Yamnaya people inherit from their ancestors?
The Yamnaya people inherited several cultural practices from the Caucasus Lower Volga people, including burial customs such as kurgan (tumulus) burials, which involved using large tombs covered by earth. This tradition reflects their shared ancestry and cultural identity, which played a crucial role in the development of their society.
How did the findings about Indo-European languages evolve due to geopolitical events?
Recent findings have been influenced by geopolitical events, notably the Russia-Ukraine conflict, which affected collaborative research efforts. While some studies utilized ancient DNA from both Russia and Ukraine, ongoing tensions have made co-authorship among scholars from these regions more challenging, impacting the dissemination of research related to Indo-European languages.
What are the implications of the new research on Indo-European languages for linguistic studies?
The implications of this new research are significant for linguistic studies, as they provide a genetic framework that unifies various Indo-European languages under a common ancestral population. This enhances our understanding of language evolution, migration patterns, and cultural exchanges throughout history.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Origin of Indo-European Languages | Identified as the Caucasus Lower Volga people in Russia, about 6,500 years ago. |
| Spread and Influence | Languages spread across Eurasia, reaching as far as Mongolia and Ireland due to the mobility of the Yamnaya peoples. |
| DNA Evidence | The research used DNA to trace the lineage of Indo-European speakers and their intermingling with local populations. |
| Genetic Research Collaboration | The studies represent a collaboration between archaeologists, linguists, and geneticists to provide a unified picture of Indo-European origins. |
| Cultural Practices | Shared burial traditions in kurgans link these ancient populations to their descendants. |
| Impact of Current Events | The Russia-Ukraine war has affected collaborative research, leading to separate studies from Russian and Ukrainian researchers. |
Summary
Indo-European languages have a rich history that connects over 40% of the world’s population today. The recent studies highlight their origins in the Caucasus Lower Volga region around 6,500 years ago, shedding light on how these languages spread across Europe and into parts of Asia. Through a combination of genetic, archaeological, and linguistic evidence, researchers have successfully pieced together the complex migration patterns and cultural practices that define the Indo-European linguistic family. With continued research, we can expect more discoveries that deepen our understanding of these languages and their impact on human culture.